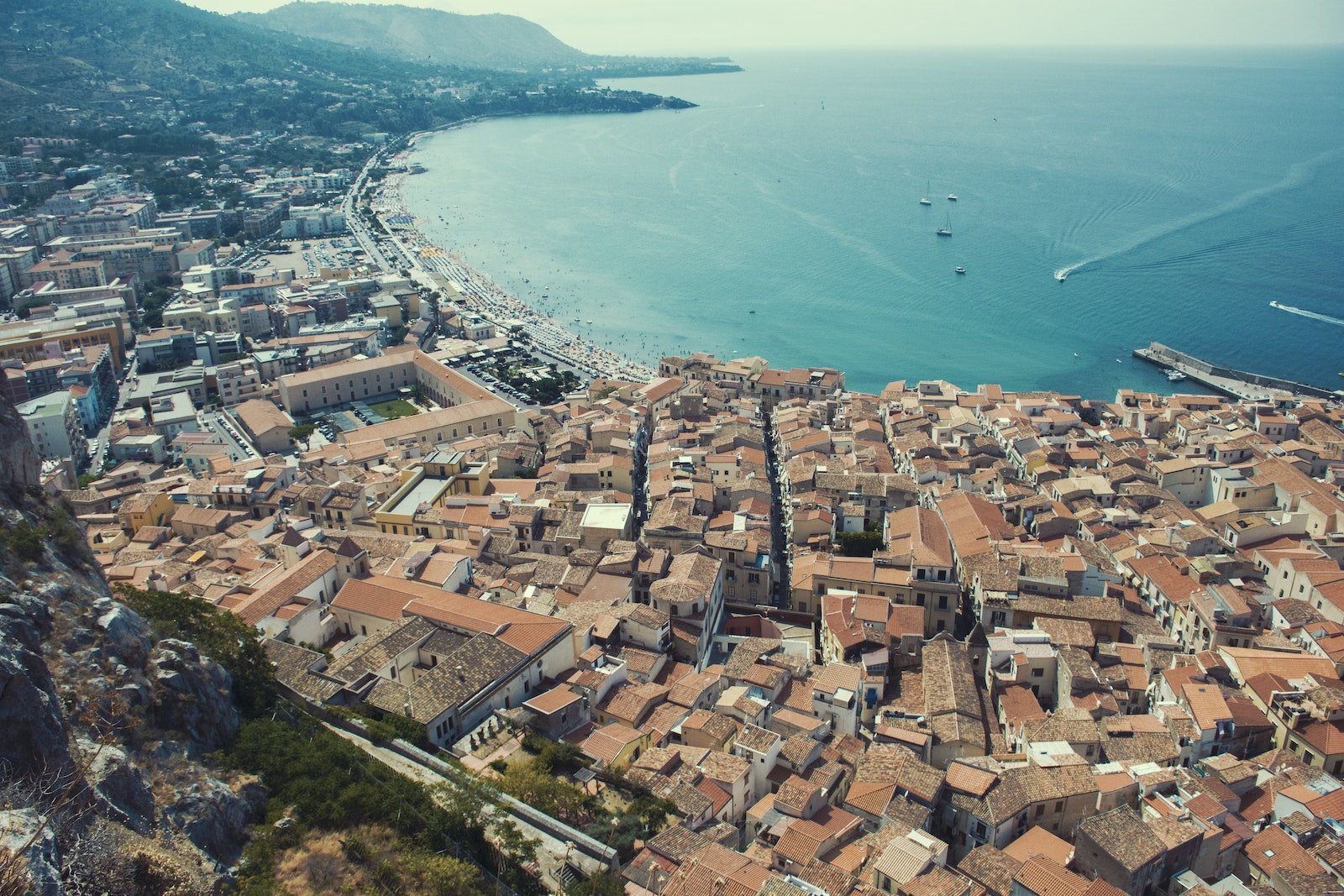
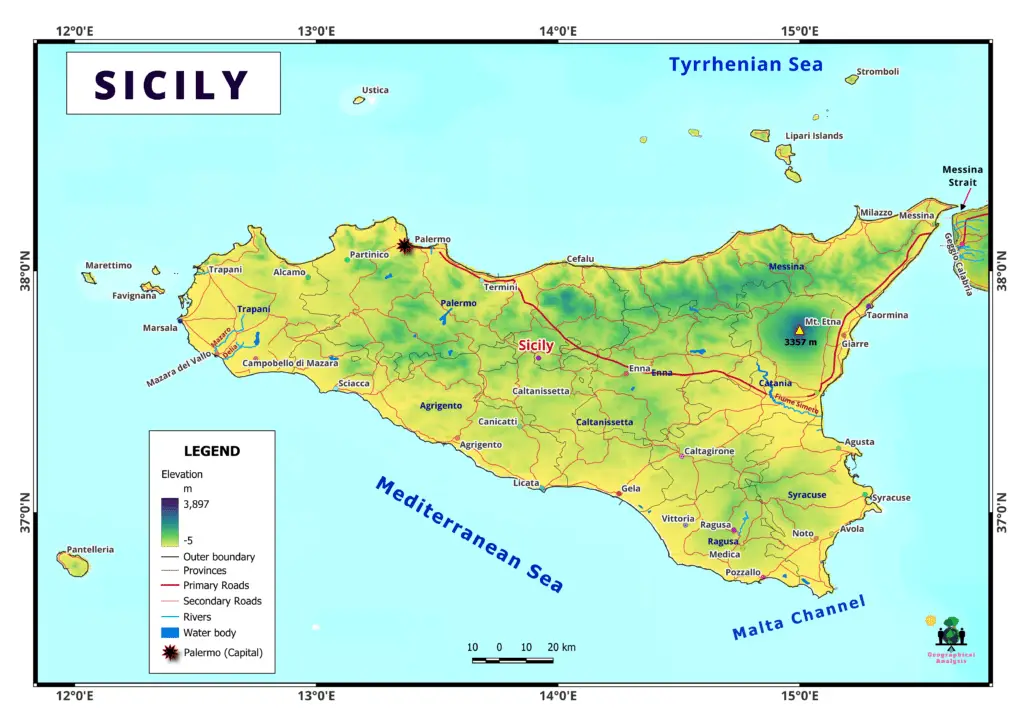
Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. The geography of Sicily is very versatile and is home to a beautiful landscape that has played an important role in the development of the region’s history, culture, and way of life. The varied landscapes of Sicily, which range from towering mountains to breathtaking coasts, each tell a story of both the island’s natural beauty and the geological wonders that can be found there. Let’s get on the road and go on an adventure to figure out the geography of Sicily and learn about its interesting characteristics.
Sicily’s rich history and diversified terrain may be attributed, in part, to the island’s strategic location, which is nestled between the Italian mainland and North Africa. This page explores the physical characteristics of the island, including its volcanic landscapes, hydrological aspects, and cultural impacts, among other topics.
Top Facts about Geography of Sicily
Below, we discuss some important facts regarding the geography of Sicily that you have to know.
1. Physical Features of Sicily
1.1. Mountainous Splendor
Mountain ranges predominate the landscape of Sicily, with the Madonie and Nebrodi Mountains being particularly prominent in the island’s northern sections. These mountains not only provide stunning vistas, but they are also home to some very special plant and animal life. The arduous topography has had an influence on the local communities as well as the traditions that have developed there.
1.2. Coastal Charms
The coastline of Sicily is more than a thousand kilometers long and has a diverse collection of beaches, bays, and cliffs along its length. The beauty of the coast is unrivaled, and it stretches all the way from the sandy coasts of Cefalù to the majestic Scala dei Turchi. The history of the fishing communities that dot the coastline is entwined with the tides and currents of the ocean.
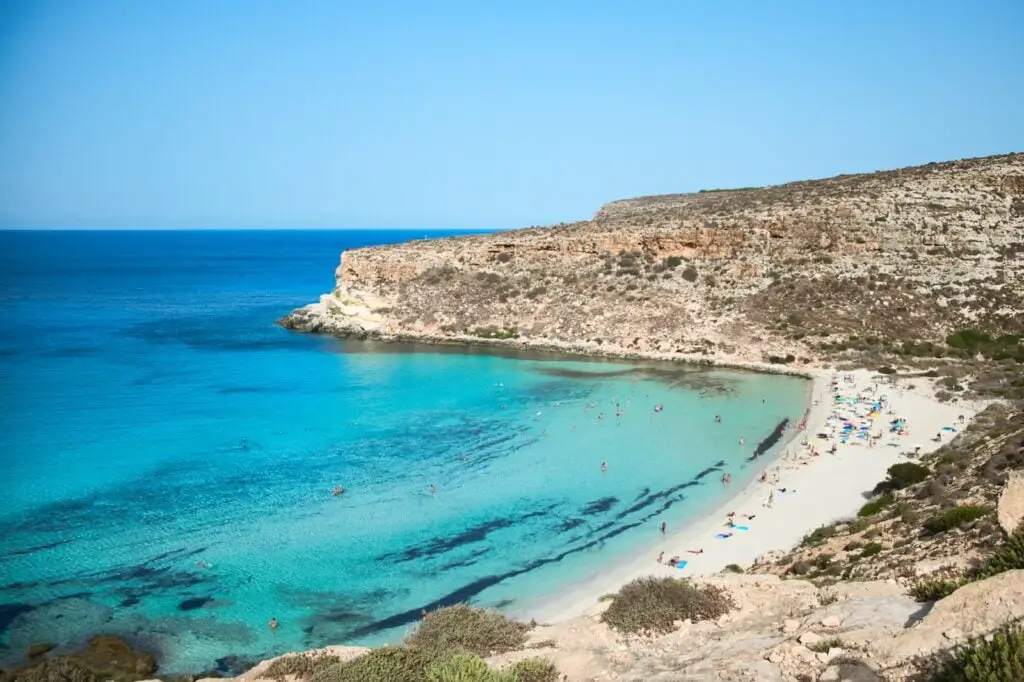

1.3. Fertile Valleys
Conca d’Oro is one of the rich valleys that may be found tucked away between the mountains and the shore. Agriculture has been practiced in these valleys for hundreds of years, and it has provided a harvest of citrus fruits, olives, and grapes. The agricultural tradition has left its imprint on the Sicilian culinary tradition, which now features flavours that are reflective of the land’s abundance.
2. Volcanic Marvels
2.1. Mount Etna: Europe’s Tallest Active Volcano
Mount Etna is a magnificent and lively volcano that may be found right in the middle of Sicily. Its towering presence has had a significant impact on the island’s history as well as its landscape. The ground has been both annihilated and improved as a result of Etna’s eruptions, which have left behind mineral-rich soil that is beneficial to agricultural practices.
2.2. Aeolian Islands: Volcanic Archipelago
The Aeolian Islands are a volcanic marvel that may be seen just off the shore of the northern coast. Active volcanoes such as Stromboli and Vulcano are among the natural wonders that have mesmerized tourists for centuries. These islands are not only a demonstration of the geological processes that have occurred on Earth but also a playground for individuals who are looking for an exciting new experience.
3. Hydrological Wonders
3.1. Rivers and Lakes
The Simeto and the Belice are only two of the rivers that have cut their way through the landscape of Sicily, helping to create the island’s distinctive topography. Earlier we said that the geography of Sicily is very rich in every aspect. In addition, the island’s tranquil lakes, such as Lake Pergusa, provide a safe haven for migrating birds and help to maintain the island’s rich biodiversity.
3.2. Ancient Aqueducts
The ancient Sicilians were very inventive, as seen in their aqueducts, which carried water and connected various parts of the island. The technological advancements of these aqueducts show that the island is capable of accommodating its topography.
4. Countryside and Urban Contrasts
4.1. Rustic Villages
The rural charm of Sicilian villages is on full display, whether they are tucked away in the hills or spread out across the lowlands. Locations such as Gangi and Savoca provide a look into traditional ways of existence, in which the surrounding environment serves as both a backdrop and a supplier.
4.2. Bustling Cities
In stark contrast to the tranquility of the countryside, towns such as Palermo and Catania are bustling with activity. Their urban environments reflect stories of various civilizations that have left their imprint via the architecture, streets, and marketplaces of the cities they inhabit.
5. Biodiversity and Flora
5.1. Mediterranean Flora
The temperature of the Mediterranean region has shaped Sicily’s flora, which includes a mix of indigenous and introduced plant species. The area is covered in a mix of olive trees, vineyards, and almond orchards, which creates a breathtakingly beautiful panorama.
5.2. Wildlife Riches
Because of the island’s varied topography, it is home to a wide variety of native animals as well as migratory birds and reptiles. Both the Zingaro Nature Reserve and the Vendicari Nature Reserve offer protected environments for these animals, which helps maintain a healthy biological balance on the island.
6. Historical Significance of Sicily

6.1. Crossroads of Civilizations
Because of its geographic location, Sicily has been a cultural melting pot for millennia. The Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, and Normans, amongst others, have all left their marks, contributing to the creation of a distinctive cultural tapestry that is evident in the architecture, language, and customs.
6.2. Architectural Influences
Sicily’s architecture is a reflection of its rich and varied past and includes everything from Greek temples to Norman churches. Because of the influence that the island’s topography had on the materials and styles that were employed, the island’s architectural legacy is one that is both beautiful and diverse.
7. Geographical Impact on Culture
7.1. Gastronomy and Agriculture
The cuisine of the island has strong roots in the island’s history and topography. The volcanic soil, Mediterranean temperature, and closeness to the sea have all had an impact on the cuisine of Sicily, helping to shape it into a gastronomic treat that is appreciated all over the globe.
7.1. Festivals and Traditions
Traditions on the island, such as the Feast of Saint Agatha in Catania and the Infiorata in Noto, have their origins in the landscape of the island. Floral displays and processions are frequently present at celebrations of the relationship between culture, faith, and the land.
8. Climate and Weather Patterns
8.1. Mediterranean Climate
The winters in Sicily are often warm and rainy, while the summers are scorching hot and arid. Because of the island’s proximity to the Mediterranean Sea, it has a climate that is conducive to the development of products like grapes, citrus fruits, and olives, all of which are now fundamental to the character of the island.
8.2. Microclimates Across the Island
The topography of the island creates several microclimates, which in turn cause fluctuations in both the temperature and the amount of precipitation. Within the confines of a single island, these variations in temperature offer a variety of one-of-a-kind experiences, from the icy summits of Mount Etna to the parched plains of the island’s southeast coast.
9. Challenges and Conservation Efforts
9.1. Erosion and Deforestation
The rough topography of Sicily is easily eroded, which has made it difficult to maintain the integrity of the land in its current state. In the past, deforestation has made these problems much worse, which is what prompted conservation initiatives to safeguard the island’s landscapes and reduce the effects of erosion.
9.2. Conservation Initiatives
The creation of national parks and reserves on Sicily is the result of ongoing efforts to preserve the island’s distinctive topography. These projects have the goals of preserving biodiversity, educating the general public, and promoting environmentally responsible tourism that takes into account the natural marvels of the island.
10. Conclusion
The dynamic forces that have molded the geography of Sicily and its landscapes, culture, and history may be seen in the island’s topography, which serves as a witness to these forces. The island is a veritable treasure trove of geographical marvels just waiting to be discovered, from the explosive eruptions of Mount Etna to the peaceful beauty of its valleys and coasts. All of these natural features may be found on the island.
11. FAQ
Is Sicily only known for its historical sites?
Although Sicily is home to a wealth of historical landmarks, the island’s topography also features a wide variety of landscapes and natural beauties that are well worth discovering. The geography of Sicily is very remarkable.
Are there any endangered species unique to Sicily?
The Sicilian fir and the Sicilian shrew are both examples of endemic species that are unique to the island yet present unique problems for their preservation.
Can I climb Mount Etna?
It is possible to walk Mount Etna with the assistance of a guided tour; however, owing to the dynamic character of the terrain, it is critical to adhere to all safety requirements.
How has the geography of Sicily influenced its architecture?
The island has been home to a number of different civilizations, each of which has added their own distinctive architectural style to its structures because of its varied topography.