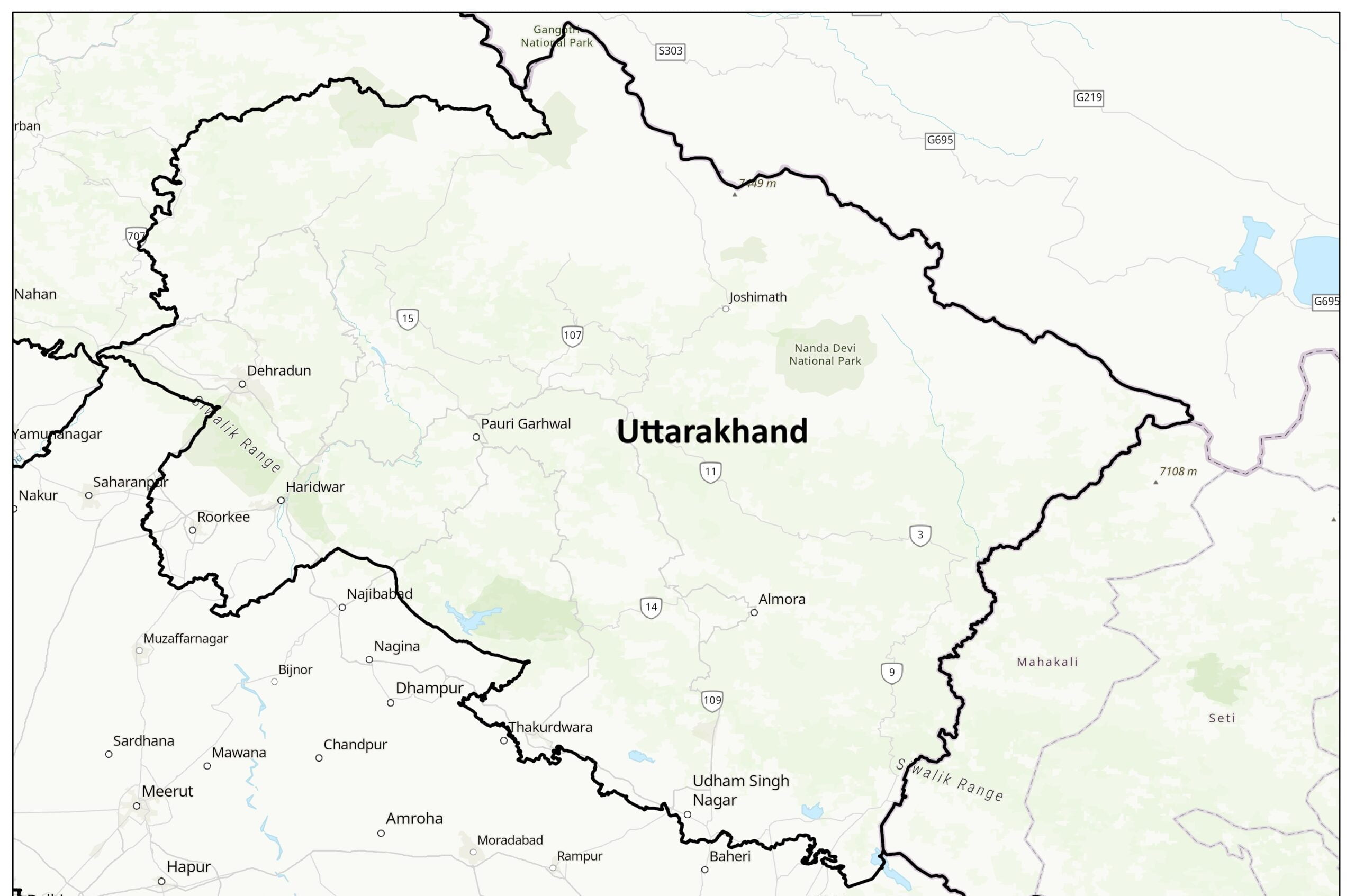
With its diverse landscape ranging from the Himalayas in the north to the plains in the south, Geography of Uttarakhand is incredible significance. Nestled in the lap of the mountains, this Indian state is home to some of the most beautiful and treacherous terrains in the country. From the glaciers of Gangotri to the rolling hills of Nainital, Uttarakhand offers a rich tapestry of natural wonders to explore and study. Let’s explore into the geography of Uttarakhand to understand the diversity and complexities that make this region truly unique.
Key Takeaways:
- Uttarakhand’s geography is characterized by its diverse terrain, ranging from the snow-capped Himalayan peaks in the north to the lush plains in the south.
- The state is renowned for its numerous rivers, including the Ganges and Yamuna, which play a vital role in the region’s irrigation and agriculture.
- Uttarakhand is home to several national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, making it a haven for biodiversity and eco-tourism.
- The state’s mountainous topography makes it prone to natural disasters such as landslides and flash floods, emphasizing the need for sustainable development practices.
- Uttarakhand attracts pilgrims from around the world due to its religious significance, with popular destinations like Badrinath, Kedarnath, and Haridwar drawing millions of visitors annually.

Physical Geography of Uttarakhand
The Himalayan Mountain Range
Clearly, the Himalayan Mountain Range plays a significant role in shaping the geography of Uttarakhand. It is home to some of the highest peaks in the world, including Nanda Devi, Trisul, and Kamet. The mountain range serves as a natural barrier, protecting the state from harsh weather conditions and influencing the climate patterns in the region.
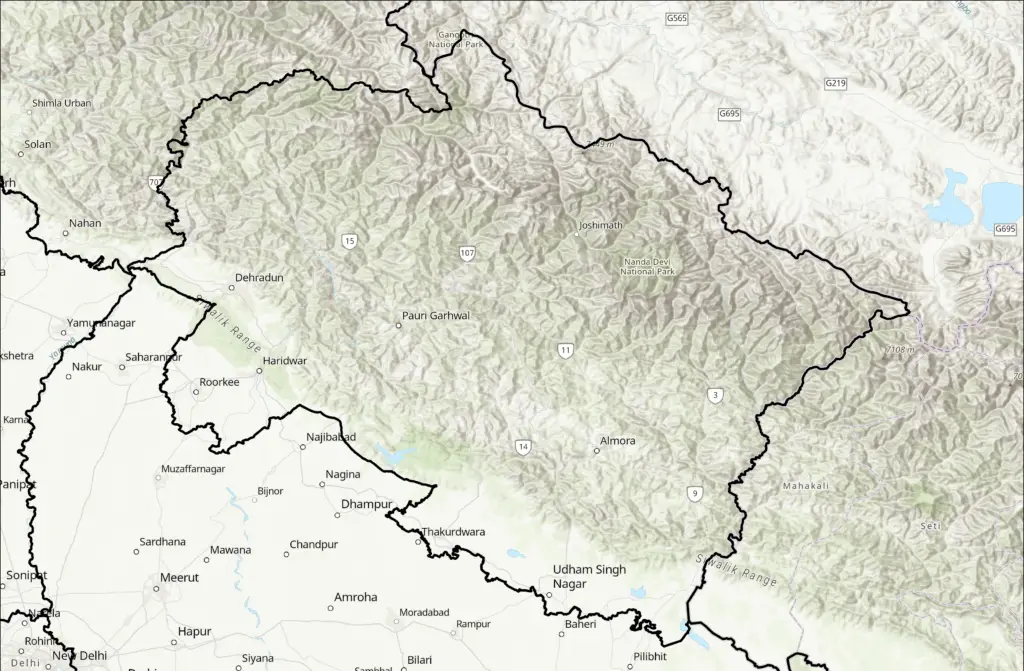
Rivers and Water Systems
Any discussion of Uttarakhand’s physical geography would be incomplete without mentioning its extensive network of rivers and water systems. The state is crisscrossed by several major rivers, including the Ganges, Yamuna, and Kali. These rivers not only provide water for irrigation and domestic use but also hold great religious significance, attracting pilgrims from all over the country.
One of the most important rivers in Uttarakhand is the Ganges, which originates from the Gangotri Glacier in the Garhwal region. The river not only sustains life in the state but also holds immense cultural and spiritual importance for the people of India. The Ganges is revered as a goddess and is believed to cleanse sins and bestow salvation upon those who bathe in its holy waters.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Seasonal Variations
Once again, Uttarakhand experiences distinct seasonal variations throughout the year. The state witnesses a temperate climate in the lower regions during summers with temperatures ranging from 20°C to 40°C. Winters, on the other hand, are cold and snowy, especially in the higher altitudes. Monsoon season brings heavy rainfall between July and September, imperative for the region’s flora and fauna.
Microclimates and Their Influence
With diverse topography, Uttarakhand showcases various microclimates that significantly influence local weather patterns. On a small scale, factors like altitude, vegetation, and proximity to water bodies create unique climatic conditions in different regions of the state. These microclimates play a vital role in sustaining a rich biodiversity and attracting tourists with varying preferences.
Climate in Uttarakhand can be harsh and unpredictable due to its mountainous terrain. While the cool summers provide relief from the scorching heat of the plains, the extreme cold winters can pose challenges for travelers. However, these varied climates also contribute to the state’s stunning landscapes and offer a wide range of activities for visitors to enjoy.
Biodiversity and Natural Habitats
Flora: Forests and Vegetation Cover
Not only is Uttarakhand known for its majestic Himalayan peaks and spiritual significance, but it also boasts rich biodiversity in terms of flora. The state is home to a diverse range of forests and vegetation cover, including alpine, temperate, and subtropical forests. These forests support a variety of plant species, contributing to the state’s overall ecological balance and natural beauty.
Fauna: Wildlife and Conservation Efforts
For wildlife enthusiasts, Uttarakhand is a paradise filled with a wide array of fauna. The state is home to several endangered species such as the Bengal tiger, Asian elephant, and snow leopard. Conservation efforts in the region, including the establishment of wildlife sanctuaries and national parks, play a crucial role in protecting these species and their natural habitats.
Natural habitats in Uttarakhand provide a safe haven for its diverse wildlife, allowing species to thrive in their untouched surroundings. The state’s mountainous terrain and lush forests provide ideal conditions for various species to flourish. However, habitat destruction due to human encroachment and climate change poses a significant threat to the ecological balance of the region.
Human Geography of Uttarakhand
Population Distribution and Demographics
To understand the human geography of Uttarakhand, it is important to look at the population distribution and demographics. Despite being a hilly state with challenging terrain, Uttarakhand has a population of over 10 million people. The state has a relatively low population density compared to other states in India, with the majority of the population residing in the plains area.
Settlements and Urbanization
To investigate deeper into the human geography of Uttarakhand, focusing on settlements and urbanization is crucial. Population in Uttarakhand is primarily concentrated in urban areas such as Dehradun, Haridwar, and Rishikesh. These cities serve as economic hubs and are experiencing rapid urbanization due to migration from rural areas.

Distribution of settlements in Uttarakhand is uneven, with a majority of the population residing in the plains due to better access to infrastructure and resources. However, it is important to note the growth of urban areas in the state, which presents both opportunities and challenges for sustainable development.
Geographical Challenges and Opportunities
Natural Disasters and Risk Management
All regions face various geographical challenges, and Uttarakhand is no exception. This beautiful state is prone to natural disasters such as flash floods, landslides, earthquakes, and forest fires. These challenges pose significant risks to human lives, infrastructure, and the environment. Effective risk management strategies are crucial to mitigate the impact of these disasters and ensure the safety and well-being of the residents.
Sustainable Development and Tourism
The picturesque landscapes of Uttarakhand offer immense opportunities for sustainable development, particularly in the tourism sector. The state is home to several prominent pilgrimage sites, national parks, and adventure sports destinations which attract tourists from around the world. However, it is crucial to balance the positive impacts of tourism with sustainable development practices to preserve the state’s natural beauty and cultural heritage for future generations.

Another critical aspect of sustainable development in Uttarakhand is the promotion of eco-tourism initiatives. By encouraging responsible travel practices and supporting local communities, the state can harness the potential of tourism as a driver for economic growth while safeguarding its fragile ecosystems. This approach not only benefits the environment but also enhances the overall visitor experience, making Uttarakhand a model for sustainable tourism development in the region.
Summing up
Hence, the geography of Uttarakhand offers a diverse and captivating landscape, from the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the lush valleys and meandering rivers. Its unique location and topography have played a significant role in shaping its cultural and ecological makeup. With a rich history and breathtaking scenery, Uttarakhand stands as a testament to the natural beauty and wonders of the Indian subcontinent.
Official website of Uttarakhand: click here