Just like a strong foundation is crucial for a sturdy building, soil health is paramount for prosperous agricultural practices. Without fertile and well-balanced soil, farmers face challenges that can jeopardize their crops and ultimately their livelihood. Soil health directly impacts crop yield, water retention, nutrient availability, and overall ecosystem balance. In this blog post, we will probe into the significance of prioritizing and maintaining healthy soil for sustainable and successful agricultural production.
Key Takeaways:
- Healthy Soil is Vital: Soil health is crucial for successful agriculture as it provides important nutrients for plant growth and supports a diverse soil ecosystem.
- Enhances Crop Resilience: Well-maintained soil health improves the resilience of crops to pests, diseases, and extreme weather conditions, leading to better yields and quality produce.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Focusing on soil health promotes sustainable agriculture practices that preserve the land for future generations and reduce the need for chemical inputs.

The Biological Components of Soil
Soil is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that is teeming with life. The biological components of soil play a crucial role in supporting plant growth and overall soil health. Understanding the various organisms present in soil can lead to better agricultural practices and improved crop yields.
Microbial Activity and Diversity
Diversity in microbial communities within the soil is crucial for nutrient cycling and overall soil fertility. The different types of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms present play key roles in decomposing organic matter, releasing nutrients, and suppressing plant diseases. A diverse microbial community can also help improve soil structure and water retention, making it more resilient to environmental stresses.
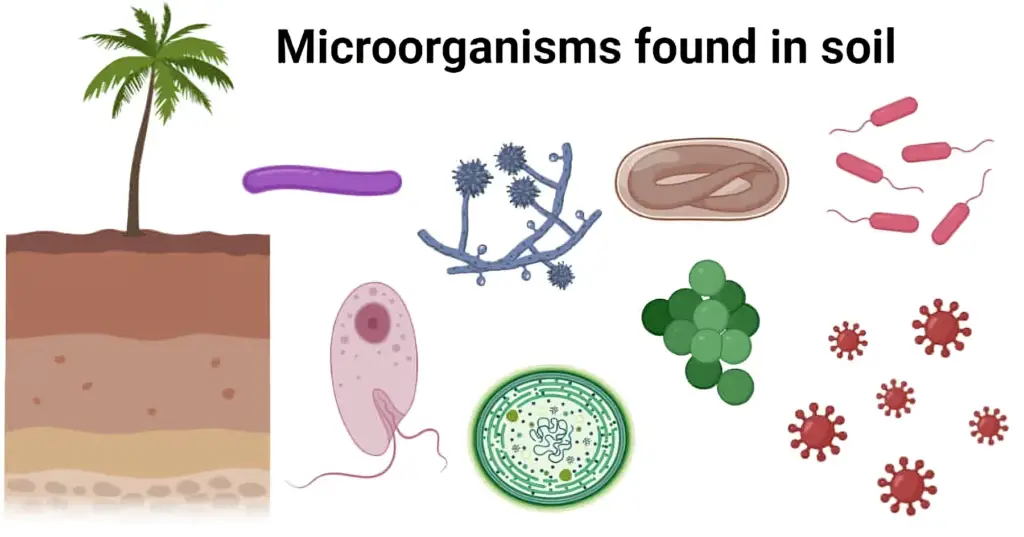
Furthermore, the activity of these microscopic organisms enhances the availability of crucial nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for plant uptake. The interactions between soil microbes and plant roots create a symbiotic relationship that is vital for healthy plant growth and development.
The Importance of Earthworms and Other Fauna
Microbial activity is not the only driver of soil health; earthworms and other soil fauna also play a critical role in maintaining soil structure and fertility. Earthworms, in particular, are ecosystem engineers that improve soil aeration, drainage, and nutrient cycling. Their burrowing activities create channels for air and water movement, which helps to alleviate compaction and improve root growth.
Any disruption to the populations of earthworms and other soil organisms can have a cascading effect on soil health and productivity. Pesticides, tillage practices, and pollution can all negatively impact the diversity and abundance of soil fauna, leading to degradation of soil quality. It is crucial to prioritize sustainable farming practices that support a diverse and thriving soil ecosystem for long-term agricultural success.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Healthy Soil
Once again, it is crucial to understand the physical and chemical properties that contribute to soil health in successful agriculture. These properties play a vital role in determining the fertility and productivity of the soil, ultimately affecting crop yield and quality.
Soil Texture and Structure
Physical properties such as soil texture and structure are key components of healthy soil. Soil texture refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles in the soil. A well-balanced soil texture with a good mixture of these particles promotes proper drainage, aeration, and root development. Soil structure, on the other hand, relates to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates or clumps. A healthy soil structure allows for good water infiltration, root penetration, and microbial activity.
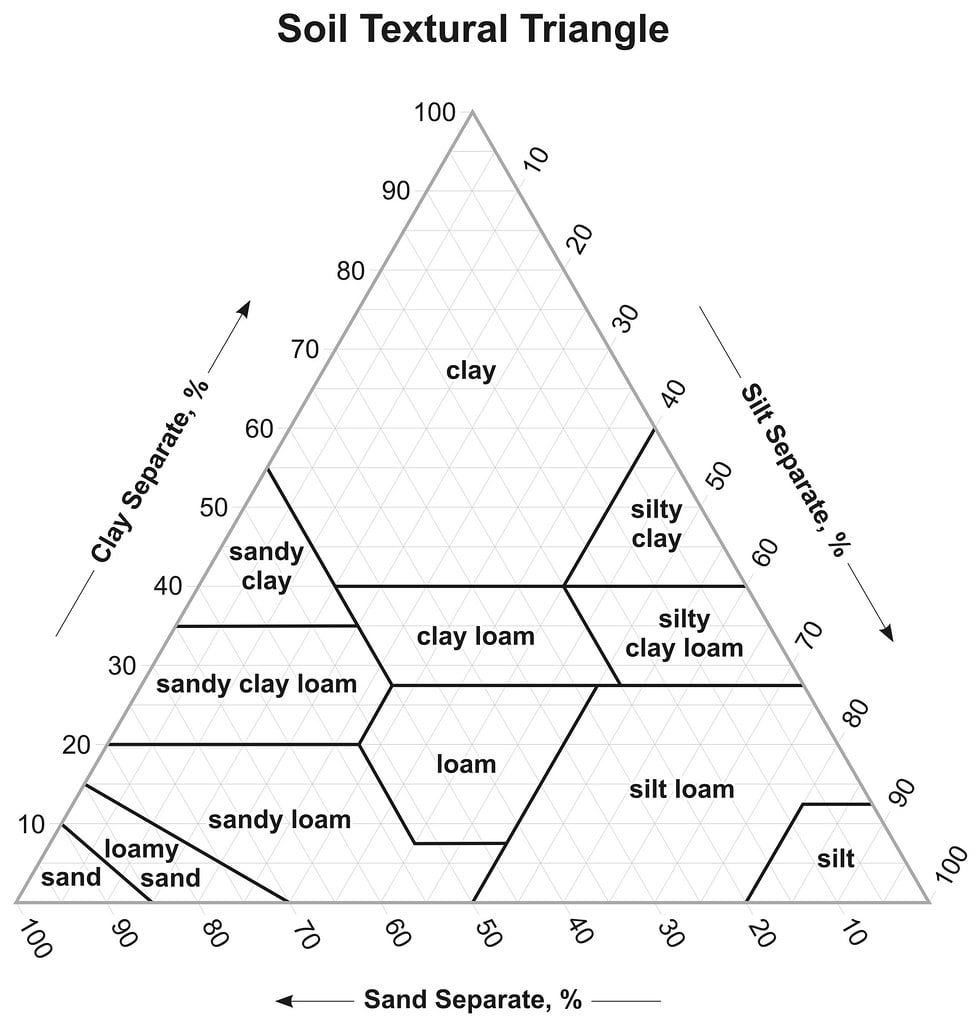
Chemical properties like organic matter content, pH balance, and nutrient availability also influence soil health. Organic matter contributes to soil fertility by providing crucial nutrients for plant growth and improving soil structure. The pH balance of the soil affects nutrient availability to plants; different crops have specific pH requirements for optimal growth. Nutrient availability, including macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, is crucial for plant development and overall soil fertility.
Nutrient Content and pH Balance
Physical factors like nutrient content and pH balance are critical for healthy soil. Nutrient content refers to the availability of crucial elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the soil. These nutrients are vital for plant growth and development. The pH balance of the soil influences nutrient availability; a pH that is too high or too low can limit the uptake of crucial nutrients by plants.

With the right balance of nutrients and a proper pH level, plants can thrive and achieve their maximum growth potential. It is crucial to regularly test and monitor soil nutrient levels and pH balance to make informed decisions about fertilizer applications and soil amendments. By maintaining optimal soil health through proper nutrient management and pH adjustments, farmers can ensure successful crop production and sustainable agriculture practices.
Farming Practices That Promote Soil Health
Crop Rotation and Diversity
Keep soil healthy and productive by implementing crop rotation and diversity in farming practices. Planting different crops in a sequenced order helps prevent the depletion of specific nutrients from the soil and reduces the build-up of pests and diseases that target a single crop species. Additionally, diverse crop rotations can improve soil structure and enhance the soil‘s ability to retain water and nutrients.
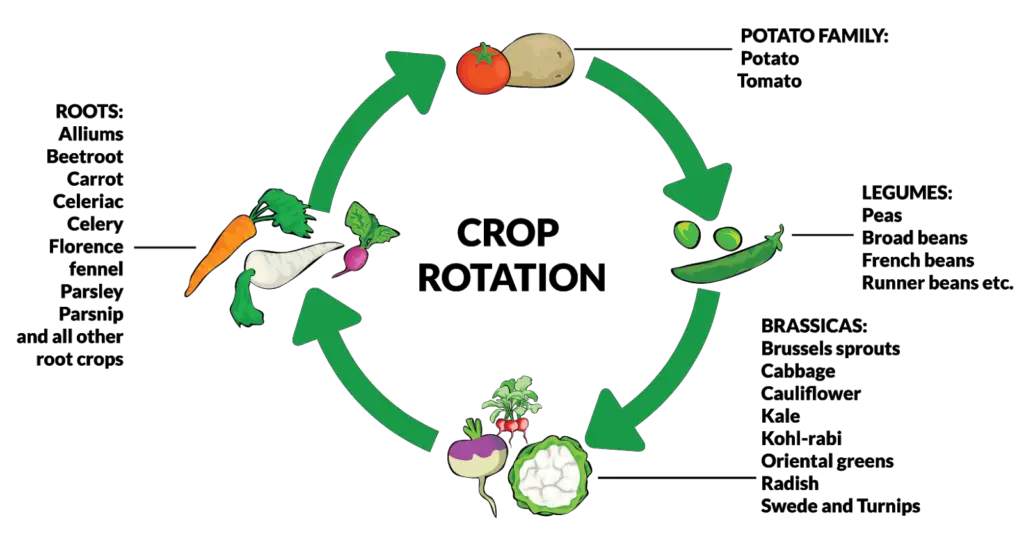
By rotating crops, farmers can also increase biodiversity above and below the soil surface. Different crops attract various beneficial insects, microbes, and soil organisms, creating a balanced ecosystem that supports soil health. This practice not only boosts soil fertility but also reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, promoting a more sustainable agricultural system.
Organic Matter Management and Composting
The organic matter is a crucial component of soil health as it provides nutrients, improves soil structure, and enhances soil biodiversity. The incorporation of organic matter through practices such as composting not only increases soil fertility but also reduces erosion and promotes water retention in the soil.

Diversity in the organic matter sources used for composting can further enhance soil health. Combining various materials such as crop residues, livestock manure, and kitchen scraps creates a nutrient-rich compost that boosts soil fertility and microbial activity. This sustainable practice supports long-term soil health and productivity, crucial for successful and environmentally friendly agriculture.
The Global Impact of Soil Conservation
Not only is soil health important at a local level for individual farmers, but it also has far-reaching global implications. The conservation of soil plays a vital role in sustaining agricultural productivity, ensuring food security, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Soil Erosion and Its Effects on Agriculture
To understand the importance of soil conservation, we must first recognize the detrimental effects of soil erosion on agriculture. Soil erosion, caused by factors such as water, wind, and human activities like deforestation and poor land management, results in the loss of topsoil. This loss of fertile topsoil can lead to decreased crop yields, reduced agricultural productivity, and increased vulnerability to droughts and floods.

Soil erosion not only affects the quantity of food produced but also impacts its quality. Sediment runoff from eroded soils can pollute water sources, harming aquatic ecosystems and human health. Additionally, the loss of soil nutrients due to erosion necessitates the increased use of fertilizers, leading to environmental degradation and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security
The implementation of sustainable agricultural practices is crucial for addressing the challenges posed by soil erosion and ensuring food security for the growing global population. By promoting techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, conservation tillage, and agroforestry, farmers can maintain soil health, enhance biodiversity, and improve resilience to climate change.
The adoption of sustainable agriculture not only benefits farmers by increasing their long-term productivity and profitability but also contributes to global food security by ensuring stable and diverse food production systems.
Effects It is evident that soil conservation is not just a local issue but a global imperative. By prioritizing soil health through sustainable agricultural practices, we can safeguard the future of agriculture, mitigate climate change, and ensure food security for generations to come.
Final Words
Considering all points, it is evident that soil health is a foundational aspect of successful agriculture. By nurturing the soil and maintaining its health, farmers can ensure optimal crop growth, nutrient availability, and water retention. Implementing sustainable practices, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage, can significantly contribute to improving soil health and ensuring long-term productivity. It is crucial for farmers and policymakers to prioritize soil health in agricultural practices to mitigate environmental degradation, enhance food security, and sustainably meet the demands of a growing population. Ultimately, investing in soil health is investing in the future of agriculture and the well-being of our planet.
FAQ
Q: What is the importance of soil health in successful agriculture?
A: Soil health is crucial in successful agriculture because it supports plant growth by providing crucial nutrients, water, and anchorage. Healthy soil also promotes beneficial microbial activity, which contributes to disease suppression and overall plant health.
Q: How can farmers improve soil health on their farms?
A: Farmers can enhance soil health through practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, minimal tillage, and the use of organic amendments. These practices help maintain soil structure, increase organic matter content, and improve nutrient availability, leading to better crop yields and sustainability.
What are the consequences of neglecting soil health in agriculture?
A: Neglecting soil health can result in decreased crop productivity, increased vulnerability to pests and diseases, and soil erosion. Poor soil health can also lead to decreased water infiltration and retention, impacting water quality and availability. Sustainable farming practices that prioritize soil health are crucial for long-term agricultural success and environmental stewardship.