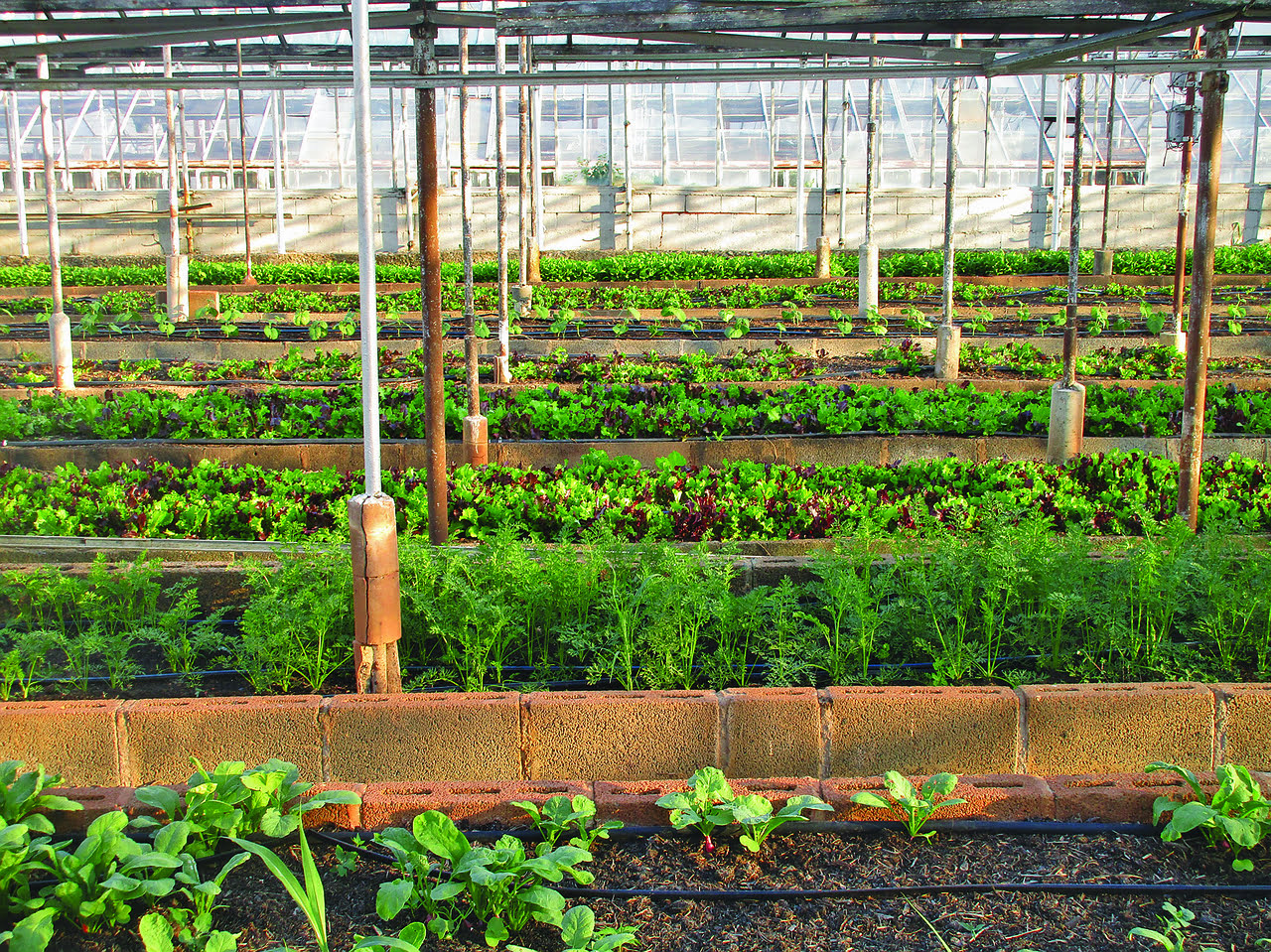
There’s a growing movement towards urban agriculture as a solution to increasing food demands and environmental challenges. In our exploration of the future of urban agriculture, we research into the innovative technologies, sustainable practices, and community benefits that are reshaping the landscape of farming in urban spaces. From vertical farms to rooftop gardens, this article examines the opportunities and challenges that come with this transformative approach to food production in cities. Join us as we uncover the potential impact of urban agriculture on our food systems and urban environments.
Key Takeaways:
- Innovative Techniques: Urban agriculture is evolving with advancements in techniques such as vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics. These methods are paving the way for sustainable and efficient food production in urban areas.
- Community Engagement: Urban agriculture fosters community engagement by bringing together people of diverse backgrounds to participate in growing and sharing food. This strengthens social ties and promotes a sense of ownership and pride in local food production.
- Sustainability and Resilience: Urban agriculture plays a key role in promoting sustainability and resilience in cities by reducing food miles, increasing local food security, and minimizing environmental impact. It contributes to a more self-sufficient and healthier urban ecosystem.

The Current State of Urban Agriculture
Urban agriculture is experiencing a renaissance as cities around the world grapple with issues of sustainability, food security, and the impact of climate change. It is a multifaceted approach to growing and distributing food within cities, utilizing various techniques such as rooftop gardens, aquaponics, vertical farming, and community gardens.

The movement towards urban agriculture is driven by a growing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional agriculture, as well as the desire to create more resilient and self-sufficient communities. The current state of urban agriculture is a mix of grassroots initiatives, government policies supporting local food production, and technological advancements that are revolutionizing how food is grown and distributed in urban areas.
Technological Innovations
With the advent of technologies such as LED lighting, hydroponics, and precision farming, urban agriculture has undergone a transformation in recent years. The integration of these technologies has allowed for year-round production, increased crop yields, and the ability to grow food in unconventional spaces like abandoned warehouses and underground tunnels.
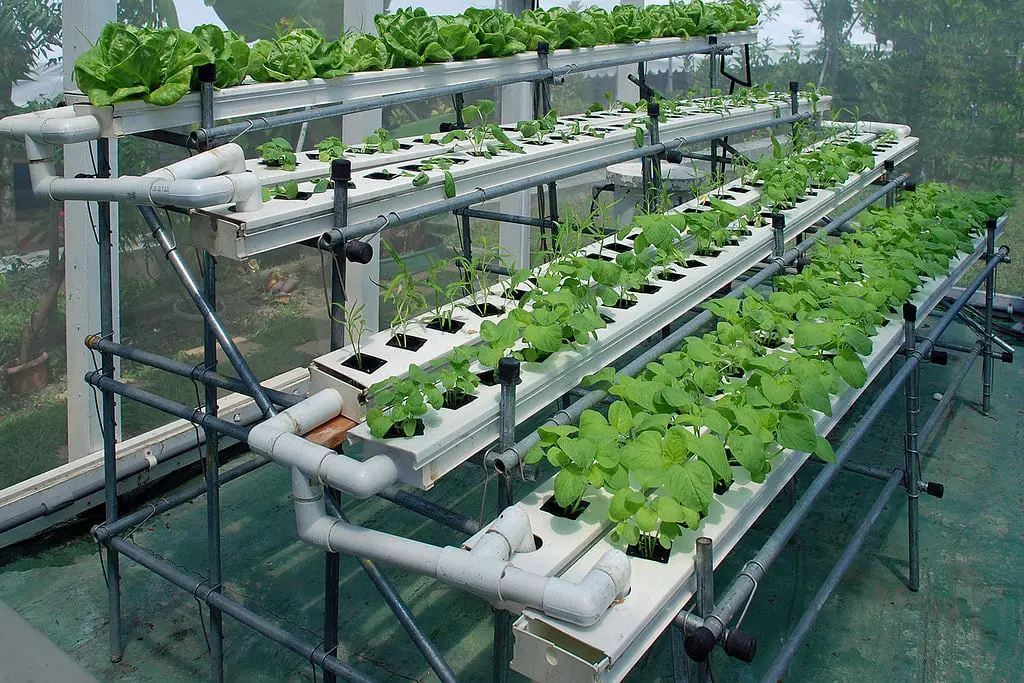

The use of data analytics and automation in urban farming has also improved efficiency and reduced the environmental footprint of food production. The combination of technology and agriculture has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about food security and sustainability in cities.
Socioeconomic Impact
Technological advancements in urban agriculture have the potential to not only transform how food is grown, but also positively impact the socioeconomic dynamics of urban communities. State of the art farming techniques create opportunities for job creation, skill development, and community engagement.
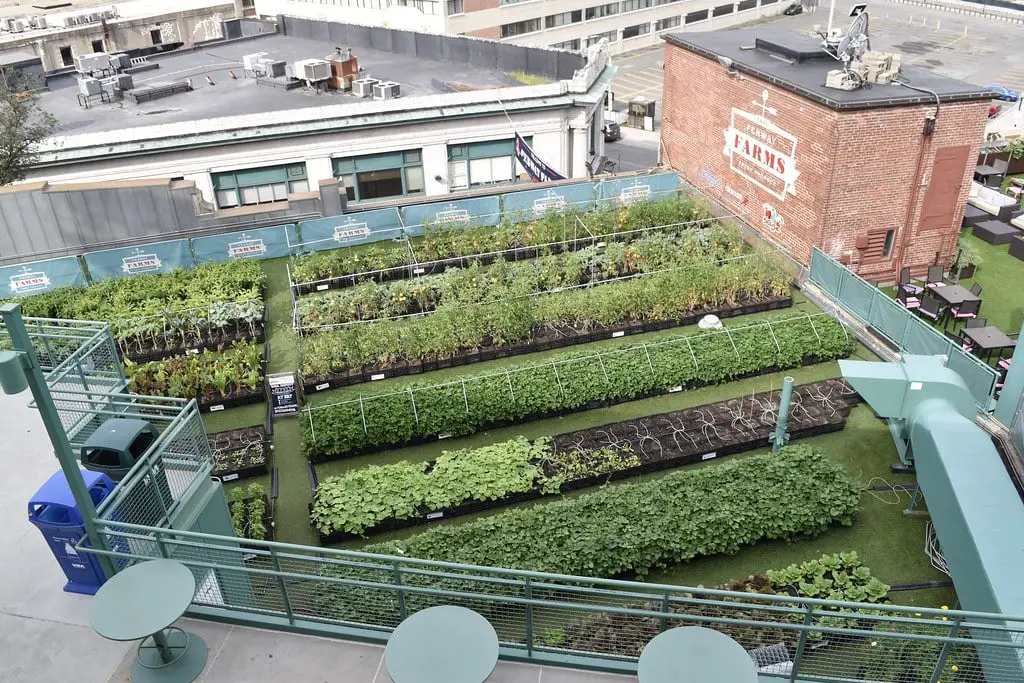
The Potential of Rooftop and Vertical Farming
To truly understand the potential of rooftop and vertical farming, we must first recognize the innovative solutions they offer to address the growing challenges of food security and sustainability in urban areas. Over the past few years, these practices have gained significant traction, providing fresh produce in the heart of cities and reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional farming and transportation.

Benefits and Challenges
One of the key benefits of rooftop and vertical farming is the maximization of limited urban space. By utilizing rooftops and vertical structures, farmers can grow food right where it is consumed, reducing the need for long-distance transportation. Additionally, these practices promote local food production, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food system. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs, technical expertise requirements, and potential limitations on crop variety and yield are hurdles that must be addressed for widespread adoption.
Implementation Strategies
Implementation of rooftop and vertical farming can be achieved through various strategies, including establishing partnerships with building owners, utilizing advanced technologies for efficient resource management, and integrating urban farming into city planning initiatives. Collaboration between stakeholders such as government agencies, urban planners, technology providers, and community organizations is crucial to drive the success of these initiatives. By leveraging collective expertise and resources, cities can create thriving urban agricultural ecosystems that benefit both the environment and the community.
Implementation of rooftop and vertical farming requires a multidisciplinary approach, blending agriculture, architecture, engineering, and sustainability principles. By fostering innovation and collaboration, cities can harness the potential of these farming practices to create a more sustainable, secure, and efficient food system for urban populations.
Urban Farming and Sustainable Development
Many cities around the world are turning to urban farming as a means of promoting sustainable development. This trend is driven by the need to address issues such as food security, environmental sustainability, and community resilience. Urban agriculture holds great potential for transforming cities into more self-sufficient and sustainable places.
Contribution to Food Security
Sustainable urban farming practices contribute significantly to food security in urban areas by providing fresh, healthy produce to city residents. By reducing the distance food travels from farm to plate, urban farming helps lower carbon emissions associated with transportation. Additionally, urban farms can utilize underutilized spaces such as rooftops, vacant lots, and community gardens to increase food production in areas where access to fresh produce is limited.
Community-based urban farming initiatives not only enhance access to fresh food but also create local employment opportunities and foster community engagement. By empowering individuals to grow their own food, urban farming projects promote self-sufficiency and food sovereignty among urban populations.
Environmental Implications
Farming in urban areas has numerous environmental implications, both positive and negative. On one hand, urban agriculture can help mitigate urban heat island effects by increasing green spaces and reducing the heat absorbed by buildings and concrete surfaces. It also promotes biodiversity and urban ecosystem resilience by providing habitats for pollinators and other beneficial organisms.
However, urban farming may also pose challenges such as soil contamination from pollutants present in urban soils. Careful monitoring and remediation efforts are necessary to ensure that urban agriculture practices do not contribute to the further degradation of soil and water quality in cities.
Policy and Community Engagement
All around the world, urban agriculture is gaining traction as a viable solution to food security, environmental sustainability, and community resilience. Policy and community engagement play a crucial role in shaping the future of urban agriculture by providing frameworks for development and fostering a sense of ownership and empowerment among residents.
The Role of Governments
On a governmental level, the implementation of supportive policies is paramount in promoting urban agriculture initiatives. By offering incentives such as tax breaks, land access, and technical support, governments can encourage individuals and organizations to participate in urban farming projects. Legislation that addresses zoning, land tenure, water rights, and food safety regulations also plays a significant role in the success and expansion of urban agriculture activities.
Fostering Community Involvement
With an emphasis on fostering community involvement, urban farming projects have the potential to transform neighborhoods and enhance social cohesion. Community gardens, farmers’ markets, and educational programs not only provide access to fresh produce but also create spaces for people to connect, learn, and collaborate. Engaging residents in the planning and decision-making processes empowers communities to take ownership of their food systems and build sustainable practices for the future.
Role: Community members are not just recipients of the benefits of urban agriculture; they are active participants in shaping the landscape and dynamics of their neighborhoods. By involving residents in every step of the process, from planning to implementation and maintenance, urban farming initiatives can effectively address local needs and foster a sense of pride and belonging within the community.
Summing up
Ultimately, the future of urban agriculture holds immense promise for transforming our cities into more sustainable, resilient, and food-secure environments. With innovations in vertical farming, aquaponics, and rooftop gardens, urban agriculture is set to play a crucial role in feeding growing urban populations while reducing food miles and environmental impact. By integrating food production into the very fabric of our cities, we can create healthier communities, improve food security, and promote a more sustainable way of living. The future of urban agriculture is indeed bright, offering a path towards a more sustainable and nourished future for all.
FAQ
Q: What is urban agriculture?
A: Urban agriculture refers to the practice of growing and cultivating food and non-food products within and around urban areas. It includes rooftop gardens, vertical farming, community gardens, and hydroponic systems.
Q: Why is urban agriculture important for the future?
A: Urban agriculture plays a crucial role in creating sustainable and resilient cities. It provides fresh produce, reduces food miles, promotes community engagement, improves air quality, and enhances urban biodiversity. Additionally, it can help address food security issues and reduce the environmental impact of traditional agriculture.
Q: What are some challenges facing the future of urban agriculture?
A: Some challenges include limited space, soil contamination, access to resources, zoning regulations, and economic viability. To overcome these challenges, urban agriculture practitioners must innovate with technology, collaborate with local governments, educate the community, and advocate for policies that support urban farming initiatives.