Many are unaware of the diverse and rich geography of Punjab, a region that holds significant historical, cultural, and agricultural importance. Located in the northwestern part of India and eastern Pakistan, Punjab is known for its fertile plains, five rivers, and vibrant culture. The region’s agricultural productivity is crucial to the economy, with rich soil and ample water supply supporting a variety of crops. However, Punjab also faces challenges such as water scarcity and pollution due to intensive farming practices. In this blog post, we will explore the geography of Punjab, highlighting key facts and features that make this region unique.
Key Takeaways:
- Location: Punjab is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent.
- Physical Features: The region is characterized by fertile plains, five rivers (Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej), and the presence of the Himalayas in the northeast.
- Climate: Punjab has a semi-arid climate with hot summers and relatively mild winters. The region experiences monsoon rains from July to September.
- Agriculture: Punjab is known as the “Granary of India” due to its highly productive agricultural sector. The main crops grown include wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane.
- Culture: The culture of Punjab is rich and vibrant, known for its music, dance (Bhangra), festivals (like Lohri and Vaisakhi), cuisine (including popular dishes like Makki di Roti and Sarson da Saag), and traditional attire (such as Punjabi suits and turbans).

Physical Geography of Punjab
Location and Borders
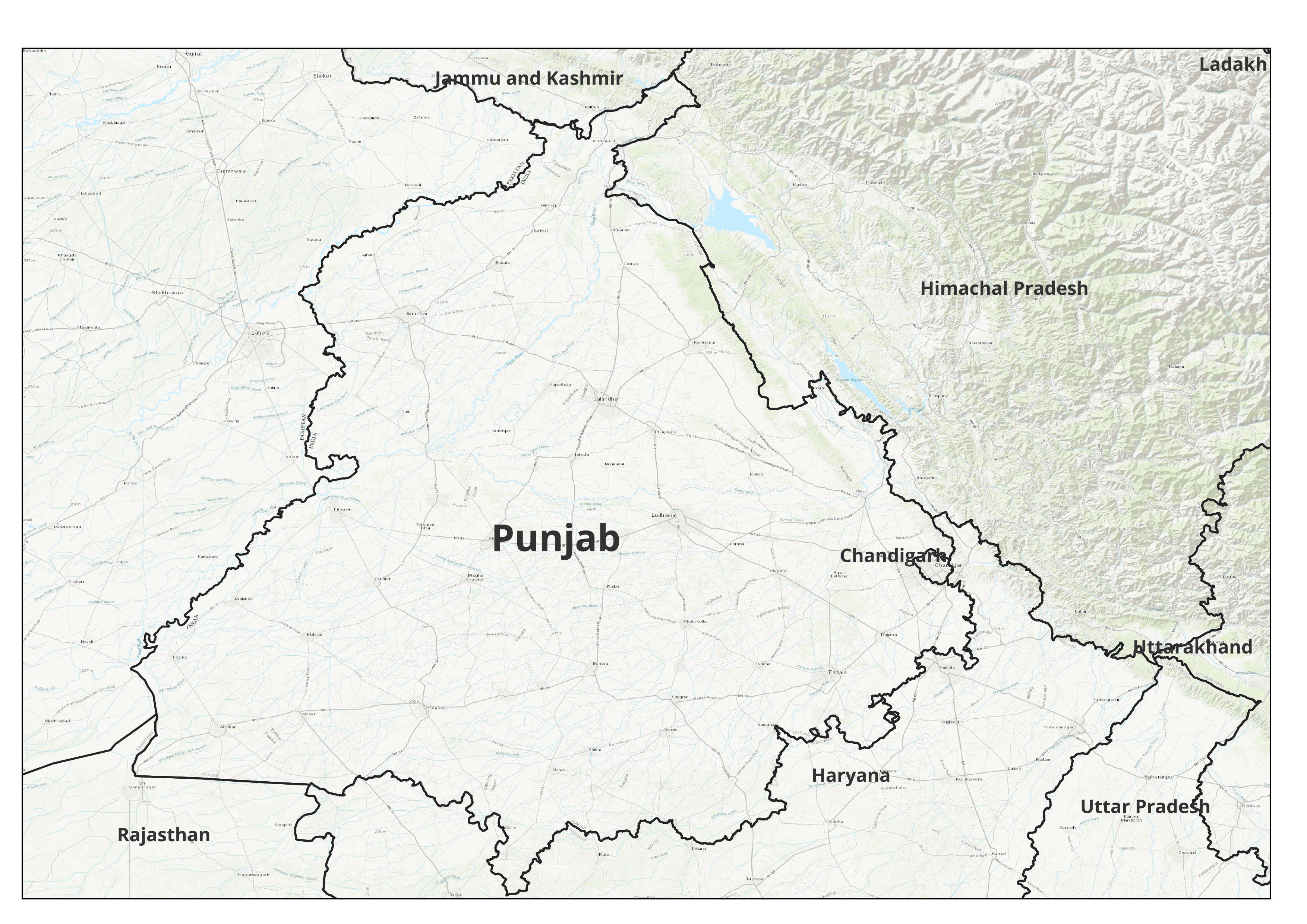
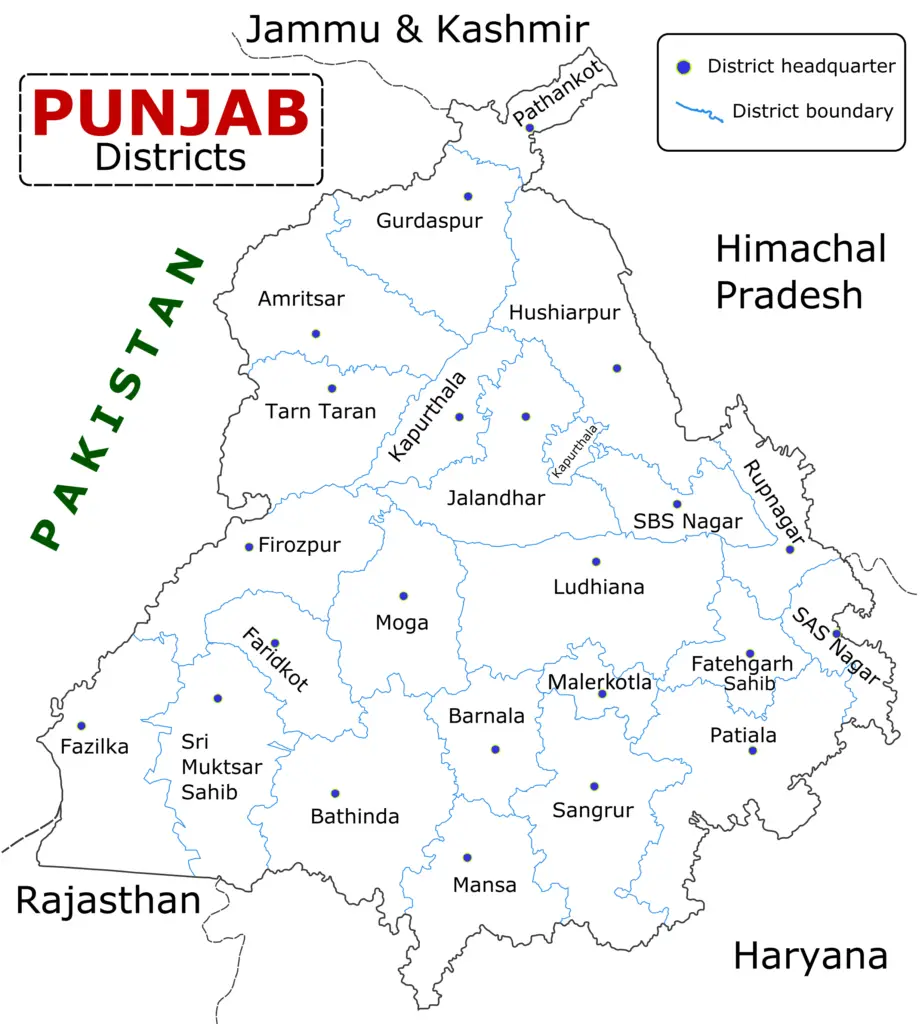
Punjab is a region in northern India, with parts also located in eastern Pakistan. It is bordered by the states of Jammu and Kashmir to the north, Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south, and Rajasthan to the southwest. In Pakistan, Punjab shares its border with the provinces of Sindh to the south, Balochistan to the southwest, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the northwest.
Topography and Climate
The topography of Punjab is mainly flat and fertile due to the presence of five major rivers, including the Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, and Sutlej. The climate in Punjab is characterized by hot summers and cold winters. The region experiences a monsoon season from July to September, with most of the rainfall occurring during this time.

To understand Punjab’s topography better, it is important to note that the agricultural productivity in the region is heavily reliant on the rivers for irrigation, making Punjab one of the most fertile regions in India. However, the flat terrain also makes it prone to flooding during the monsoon season, which can have devastating effects on the local population and infrastructure.
Human Geography of Punjab
Population Distribution
Once again, Punjab, a state in northern India, is known for its relatively high population density. The majority of the population is concentrated in the fertile plains of the region, particularly along the rivers like the Indus and its tributaries. Cities like Ludhiana, Amritsar, and Jalandhar are key population centers in the state.
Urban and Rural Dynamics
For Urban and Rural Dynamics, Punjab exhibits a unique blend of urban and rural lifestyles. The state has a high rate of urbanization, with a significant portion of the population residing in cities and towns. However, agriculture still plays a vital role in the economy, leading to a balanced mix of urban and rural dynamics.

Population in Punjab is transitioning towards urban areas, leading to rapid urban growth. This trend has both positive and negative impacts on the state. The urban areas are hubs of economic activity and offer better access to services like healthcare and education. However, this rapid urbanization also poses challenges such as increased strain on infrastructure and environmental degradation.
Natural Resources and Economy
Agricultural Significance
Economy of Punjab heavily relies on agriculture, with the region known as the “Granary of India” due to its fertile soil and extensive irrigation system. The state is a major producer of wheat, rice, sugarcane, and fruits like kinnow and mangoes. Punjab’s agriculture sector contributes significantly to the state’s economy and food supply.

Industrial and Mining Sectors
With a strong industrial base, Punjab is home to a variety of manufacturing industries including textiles, sports goods, and engineering goods. The mining sector in Punjab focuses on coal, limestone, and gypsum extraction. The state also has a growing presence in the IT and pharmaceutical industries.
Natural resources like coal and limestone play a crucial role in Punjab’s industrial growth, while the state’s agricultural prosperity provides a stable foundation for the economy. However, the over-reliance on agriculture has its challenges, making the diversification into industrial and service sectors vital for Punjab’s economic sustainability.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation Efforts
Pollution and Resource Management
Noticing the alarming rise in pollution levels due to industrialization and urbanization, Punjab faces significant challenges in managing its resources sustainably. Water pollution from industrial effluents and agricultural runoff, coupled with air pollution from vehicular emissions, pose serious threats to the environment and public health.
Conservation Policies
For effective conservation efforts, Punjab has implemented various policies and initiatives to address environmental concerns. The state government has introduced laws to regulate industrial emissions, promote sustainable agriculture practices and protect natural habitats. Efforts are being made to promote renewable energy sources and reduce reliance on non-renewable resources.
Conservation efforts in Punjab are crucial to safeguard the environment and ensure a sustainable future for the region. By enforcing stricter regulations on pollution control and resource management, the state aims to mitigate the impact of human activities on the ecosystem. Collaborative efforts between government agencies, industries and local communities are important to address environmental challenges and promote conservation practices.
To wrap up
With this in mind, the geography of Punjab plays a crucial role in shaping the region’s history, culture and economy. From its fertile plains to the majestic Himalayas in the north, Punjab offers a diverse landscape that influences everything from agriculture to tourism. Understanding the geographical features of Punjab provides valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities faced by the region. By appreciating its natural resources and topographical characteristics, we can better comprehend the unique identity and significance of Punjab in the Indian subcontinent.
Punjab official website: click here