Innovations in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology have created exciting possibilities for the future of GIS mapping and spatial analysis. As we look ahead, it is crucial to stay informed about the emerging trends and cutting-edge advancements shaping the GIS landscape. From real-time data integration to AI-driven analytics, the potential for GIS to revolutionize industries like urban planning, environmental conservation, and disaster response is immense. In this blog post, we will explore the most impactful trends and innovations that are set to redefine the field of GIS in the coming years.

Advancements in GIS Technologies
Integration with Big Data and AI
With the rapid growth of geospatial data, GIS technologies are increasingly integrating with Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to provide more robust and insightful analyses. Some cutting-edge applications include using AI algorithms to analyze satellite imagery for urban planning, employing machine learning to predict natural disasters based on geospatial patterns, and utilizing Big Data to track and combat the spread of diseases geographically.

Cloud Computing and GIS Services
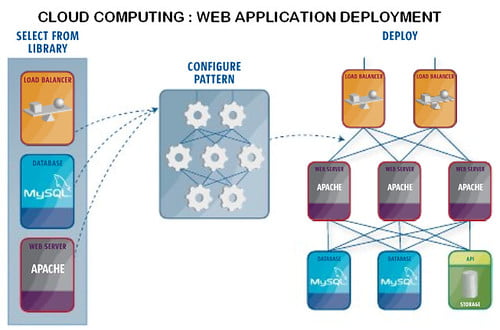
For organizations and businesses looking to streamline their GIS operations, incorporating Cloud Computing and GIS Services is becoming a game-changer. The ability to access GIS software and data storage on the cloud allows for enhanced scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in managing geospatial information. This shift towards cloud-based GIS services enables quicker data processing, efficient collaboration among remote teams, and easier integration with other cloud-based technologies.
GIS and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Real-time Data and Location Intelligence
Little did we know a few years ago that the integration of GIS with the Internet of Things (IoT) would revolutionize the way we capture, analyze, and utilize spatial data. An increasing number of sensors embedded in various devices and assets now continuously collect real-time data, providing a goldmine of information for organizations. By combining this real-time data with location intelligence through GIS, businesses can make more informed decisions promptly and respond swiftly to changing circumstances.
Smart Cities and Urban Planning
One of the most significant impacts of GIS and IoT integration is in smart cities and urban planning. With IoT sensors strategically placed throughout a city, vast amounts of data are generated daily, offering insights into traffic patterns, waste management, environmental conditions, and much more. This data is crucial for city planners and policymakers to make informed decisions for sustainable development and enhanced quality of life for residents.

Another advantage of using GIS in smart cities is the ability to create dynamic city models that simulate various scenarios based on real-time data. This simulation allows city planners to visualize the potential consequences of their decisions before implementation, leading to more efficient resource allocation and improved urban infrastructure.
Industry-Specific Innovations in GIS
Environmental Management and Conservation
For environmental management and conservation, GIS plays a crucial role in helping organizations monitor and protect natural resources. By utilizing spatial data, professionals can track changes in ecosystems, analyze deforestation patterns, and identify areas for conservation efforts. GIS enables better decision-making by providing a comprehensive view of environmental factors and their interactions.
Transportation and Logistics Optimization
To streamline transportation and logistics processes, GIS technology is revolutionizing route planning, fleet management, and delivery optimization. By incorporating real-time data on traffic patterns, weather conditions, and road closures, companies can improve efficiency and reduce costs. GIS also helps in predicting demand, optimizing inventory levels, and enhancing overall supply chain management.
With the advancement of GIS in transportation and logistics, companies can significantly reduce their carbon footprint by optimizing delivery routes, minimizing fuel consumption, and maximizing vehicle capacity utilization. This technology not only improves operational efficiency but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to logistics management.
Collaborative and Open Source GIS
The Rise of Community-Driven GIS Projects
Not only are traditional GIS tools and platforms evolving, but we are also witnessing a significant rise in community-driven GIS projects. These initiatives are powered by passionate individuals and groups who collaborate to create and share geospatial data and tools. This grassroots approach fosters innovation and inclusivity in the GIS domain, promoting the democratization of geospatial technology.
Emerging Platforms and Tools in Open Source GIS
With the increasing popularity of open source GIS, we are witnessing the emergence of new platforms and tools that offer robust capabilities and flexibility for geospatial analysis and visualization. From QGIS to GRASS GIS, these platforms provide powerful alternatives to proprietary software, enabling users to access a wide range of functionalities for their spatial data needs.
This shift towards open source GIS not only reduces dependency on costly proprietary software but also encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing within the geospatial community. Open source platforms empower users to customize their workflows, contributing to a more dynamic and innovative GIS landscape. Whether you are a seasoned GIS professional or a novice enthusiast, exploring these emerging platforms can expand your skill set and enhance your spatial analysis capabilities.
Educational and Career Trends in GIS
Evolving GIS Curriculum and Training Programs
To meet the demands of the rapidly evolving GIS landscape, educational institutions and training providers are continuously updating their curriculum and training programs. Integrating emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and remote sensing into GIS courses is becoming increasingly common. This ensures that students are equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to tackle the challenges of modern geospatial analysis and visualization.
GIS Professional Development and Job Market Outlook
One of the key trends in GIS is the emphasis on continuous professional development to stay relevant in the competitive job market. Professionals are encouraged to pursue certifications, attend workshops, and engage in networking opportunities to enhance their skills and expand their career prospects. With the increasing integration of GIS in various industries such as urban planning, disaster management, and environmental conservation, the job market for GIS professionals is expected to remain robust.
With advancements in technology driving the demand for GIS professionals, individuals with expertise in geospatial analysis and data visualization are well-positioned for lucrative and fulfilling careers. However, the field is also becoming more competitive, requiring professionals to stay current with the latest trends and technologies to stand out in the job market.
Final Words
To wrap up, the future of GIS is poised for continued growth and innovation as technology advances and data availability increases. Trends such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud-based systems, and mobile applications will propel GIS to new heights, providing more efficient and insightful ways to analyze spatial data. By staying current with these trends and embracing new technologies, GIS professionals can harness the full potential of geospatial information and make meaningful contributions to various industries and fields. It is crucial for GIS practitioners to continuously adapt and evolve to keep pace with the ever-changing landscape of geospatial technology, ensuring that they remain at the forefront of innovation and development in the field of GIS.