You, as a mapping professional, understand the significance of accurate data and efficient GIS tools available in the world. In this blog post, we will introduce you to 5 indispensable GIS tools that will not only streamline your mapping projects but also enhance the precision and quality of your work. These tools are vital for creating detailed maps, analyzing spatial data, and leveraging geospatial technology effectively. Whether you are a seasoned GIS expert or a novice in the field, incorporating these vital GIS tools into your workflow will undoubtedly elevate your mapping endeavors to new heights.
Desktop GIS Software
Features and Benefits
Any GIS professional knows the power and flexibility that desktop GIS software provides. These tools offer a robust set of features that allow users to analyze and visualize spatial data effectively. Desktop GIS software enables professionals to create detailed maps, perform complex spatial analysis, and communicate their findings with stakeholders.
Top Desktop GIS Applications
An imperative tool in a mapping professional’s arsenal is desktop GIS software. Desktop GIS applications such as Esri’s ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo Pro offer a wide range of functionalities that cater to different needs and skill levels. These applications provide users with the ability to work with various data formats, create stunning maps, and automate workflows to streamline their mapping projects.
Learn whether QGIS or ArcGIS is better suited to your needs. With desktop GIS applications, users can leverage advanced geoprocessing tools, access a vast repository of spatial data, and customize their mapping projects to suit specific requirements. These software solutions empower mapping professionals to make informed decisions, solve complex spatial problems, and showcase their analysis in a visually compelling manner.
Web Mapping Services
Advantages of Cloud-Based Mapping
There’s no denying the numerous advantages of utilizing cloud-based mapping technologies for mapping professionals. Mapping in the cloud allows for seamless collaboration, real-time data updates, and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. This eliminates the need for expensive hardware and software installations, making it a cost-effective solution for organizations of all sizes.
Leading Web Mapping Service Providers
Leading web mapping service providers such as Google Maps, ArcGIS Online, and Mapbox offer a wide range of tools and functionalities for mapping professionals. These platforms provide high-quality mapping data, customizable mapping styles, and integration options with other data sources. To stay ahead in the field of GIS, mapping professionals can leverage these platforms to create stunning and informative maps that can be easily shared and embedded into websites or applications.
Data Collection and GPS Tools
Integrating GPS with GIS for Enhanced Data Collection
All mapping professionals understand the importance of integrating GPS technology with GIS for enhanced data collection. Using GPS devices in conjunction with GIS software allows for precise mapping and accurate location-based data collection. This integration streamlines the process of gathering spatial information in the field, ensuring that the data captured is accurate and up-to-date.

Essential GPS Tools for Field Data Gathering
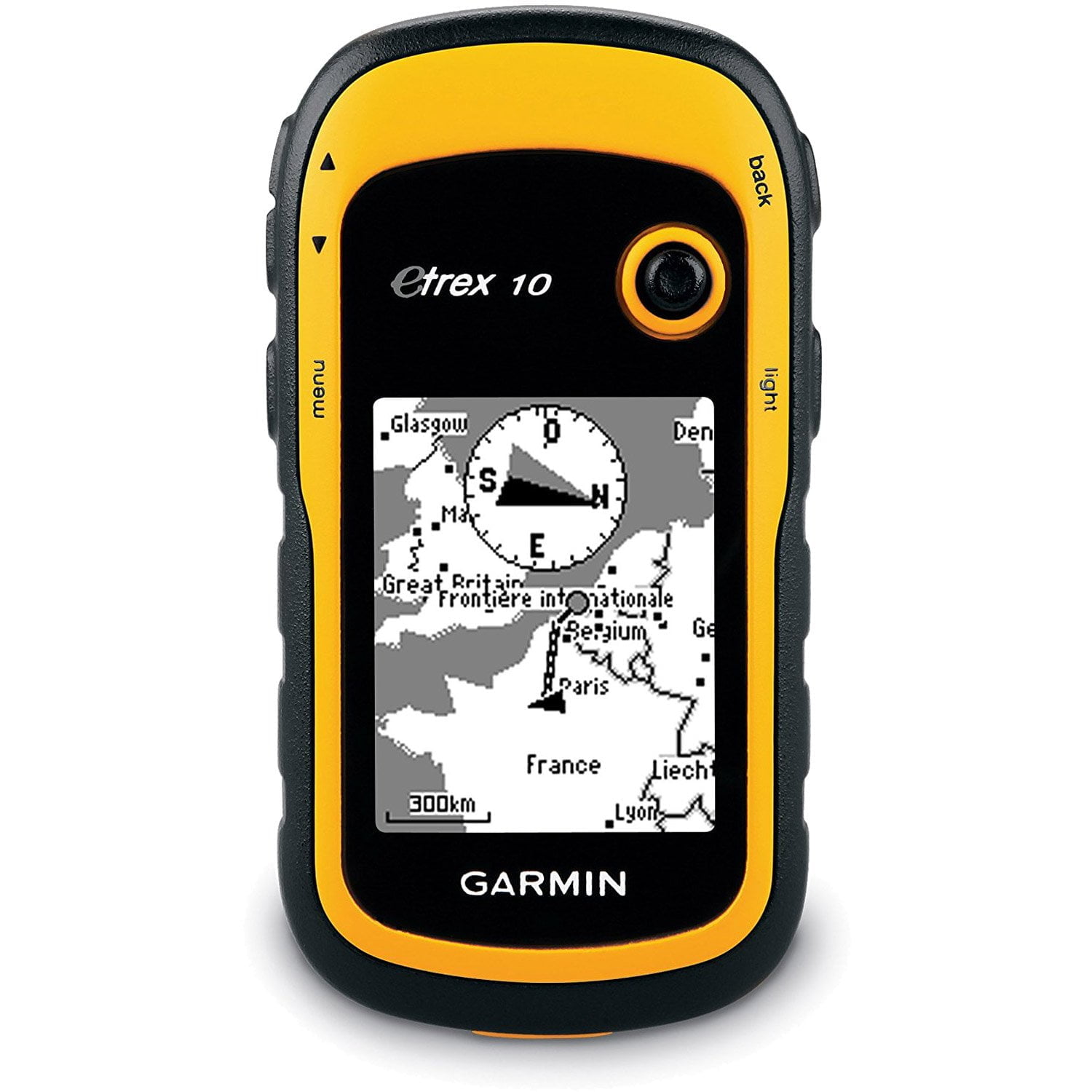
An crucial aspect of a mapping professional’s toolkit is a set of GPS tools specifically designed for field data gathering. These tools include handheld GPS devices, mobile mapping applications, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with GPS technology. Having access to these tools enables mapping professionals to collect data efficiently and accurately, even in challenging environmental conditions.
For instance, handheld GPS devices are valuable for conducting ground surveys and capturing point data with precision. Mobile mapping applications allow professionals to collect data using smartphones or tablets, increasing flexibility and accessibility in the field. UAVs equipped with GPS technology offer the ability to capture aerial imagery and topographic data from hard-to-reach areas, enhancing the overall data collection capabilities of mapping professionals.
Spatial Data Analysis Tools
Advanced Analysis Capabilities
- Data Mining: Extracting patterns from large datasets
- Geostatistics: Analyzing spatial variability and creating prediction models
- Network Analysis: Studying connectivity and flows within a network
- Spatial Regression: Understanding relationships between variables and spatial patterns
After acquiring spatial data, mapping professionals often need to dive deeper into their analysis to derive meaningful insights. This is where advanced analysis capabilities come into play.
Software Options for Spatial Data Analysis
Data analysis in the field of GIS is crucial for professionals to make informed decisions based on spatial relationships and patterns. There are several software options available that cater to different needs and expertise levels.
The choice of software tool plays a significant role in the efficiency and accuracy of spatial data analysis. Some software options offer more advanced features and flexibility, while others are more user-friendly and suitable for beginners. Professionals must consider their specific requirements and skill level when selecting the right tool for their spatial analysis tasks.
Mobile GIS Applications
Mobile GIS on the Go
On-the-go professionals in the mapping industry require robust tools that provide real-time data and seamless navigation. Mobile GIS applications offer mapping professionals the flexibility to collect, analyze, and visualize geospatial data right from their smartphones or tablets. With the convenience of mobility, experts can access critical information in the field, make informed decisions, and update maps instantly.

Popular Mobile GIS Tools for Fieldwork
Applications such as ArcGIS Collector, QGIS, and Fulcrum are popular mobile GIS tools for fieldwork that cater to the diverse needs of mapping professionals. These tools allow users to capture geotagged photos, record GPS tracks, and fill out customizable forms on the go. With offline capabilities and synchronization features, mapping experts can work efficiently even in remote areas where internet connectivity may be limited.
With intuitive interfaces and advanced functionalities, mobile GIS tools enhance productivity and accuracy in field data collection. Professionals can overlay various data layers, conduct spatial analysis, and share findings with stakeholders in real time, revolutionizing the way mapping projects are managed.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the use of GIS tools is vital for mapping professionals to effectively analyze, visualize, and interpret spatial data. The five must-have GIS tools discussed in this article – ArcGIS, QGIS, Google Earth Pro, MapInfo, and Carto – offer a range of functionalities that cater to different mapping needs. By leveraging these tools, mapping professionals can streamline their workflow, make informed decisions, and communicate spatial information effectively. It is crucial for mapping professionals to stay updated with the latest GIS tools and technologies to enhance their mapping capabilities and stay ahead in the field of geospatial analysis.